Enterprises
from various sectors these days use 3D printing technologies regularly
to obtain solid three-dimensional items from three-dimeansional digital
models. The 3D printers produce a variety of objects and items by
depositing thin layers of filament in succession. Based on the nature
and requirements of a project, every user has the option to choose from a
wide variety of 3D printers and 3D printer filaments.

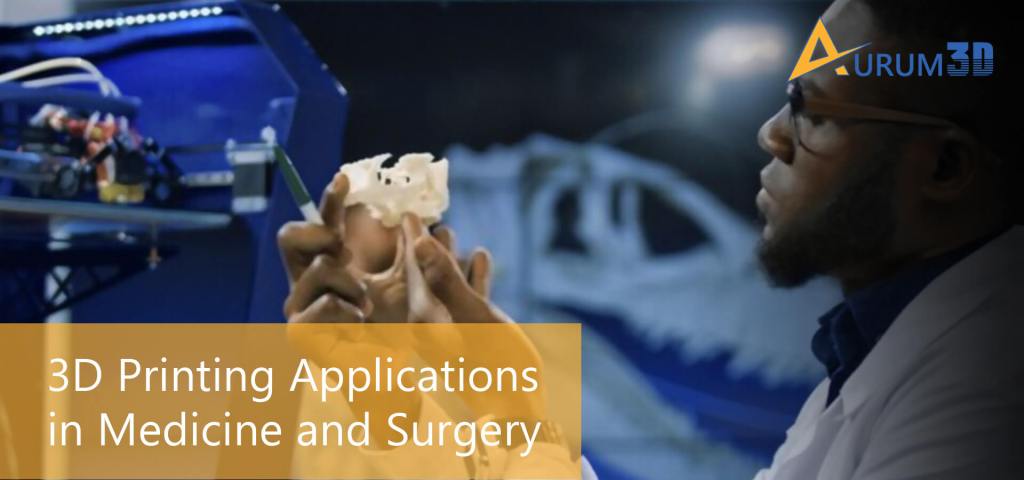
Like other industries, the healthcare industry leverage 3D printing technologies to provide patients with a completely new form of treatment and care. Surgeons these days use 3D printers while planning surgeries, while the manufacturers leverage 3D printing while planning and producing surgical equipment.
According to Yale Medicine, “Some Yale Medicine surgeons now routinely use 3D printing (essentially producing a solid, three-dimensional object from a virtual digital model) to plan surgeries, design tools specific to an upcoming surgery and that particular patient’s anatomy, and even to print some of the parts used to replace defective ones in the body.”
The 3D printing application in medicine and surgery is multiple as well as diverse. The surgeons have been creating new use cases regularly by using 3D printing technologies in innovative ways. They even explore ways to leverage the benefits of additive manufacturing technology to improve surgeries and medical care. We can understand the 3D printing application in medicine and surgery based on some innovative use cases.
Use Cases That Depict 3D Printing Application in Medicine and Surgery
Preoperative Consultation
Before
performing complex surgery, surgeons need to explain important aspects
of the surgery to patients in a simpler and clearer way. The imaging
data often requires the surgeon to put in extra time and effort to
explain complex surgical procedures to patients. 3D printing helps
surgeons to simplify preoperative consultation by producing patient
education models based on 3D imaging data. The surgeons can further use
the 3D-printed models to form strategies and choose techniques.
Surgical Planning
Many surgeons these days use 3D printers to produce models of organs physically from digital files. They use these 3D-printed organs to plan complex surgeries by identifying and addressing key challenges. At the same time, the 3D-printed organs help surgeons to teach medical students and residents how to plan and perform surgeries successfully. Some surgeons these days use sophisticated 3D printers to replicate organs during surgical planning in an affordable and cost-efficient way.
Personalized Implants
As commonly used medical devices, implants replace, support, or enhance a person’s mission/damaged biological structure. But a person’s biological structure can be replaced accurately and seamlessly only when the implant is personalized fully. One of the common applications of 3D printing in medicine and surgery is the creation of personalized implants. Many companies already use 3D printing technologies to create personalized implants for individual patients and complex cases.
Personalized and Precision Medicine
In addition to personalizing treatment and care, 3D printing technologies will soon facilitate precision medicine delivery. Many hospitals already use 3D printers to prepare personalized doses and delivery systems based on a patient’s age, lifestyle, body size, and sex. Precision medicine can be produced by a physician, nurse, or pharmacist who knows how to use a 3D printer. In addition to delivering highly personalized medicine to every patient, 3D printing will help hospitals to save both funds and resources.
Three-Dimensional Bioprinting
According to Science.org.au, “Bioprinting can produce living tissue, bone, blood vessels and, potentially, whole organs for use in medical procedures, training, and testing.” Both bioprinting and 3D printing are additive manufacturing processes. 3D printing technologies produce a variety of items using plastic-bases, resin-based, or powder-based filaments. On the other hand, bioprinting technologies produce organ-like structures using biomaterials and cells.
Many healthcare companies these days leverage professional 3D printing servicesto transform bioprinting. They adopt three-dimensional bioprinting to produce bone, living cells, and tissues using biomaterials as inks. The physicians and surgeons can leverage bioprinting to produce personalized tissues and cells for individual patients. The personalized tissues and cells enable physicians to deliver personalized and targeted treatment to every patient.
Innovative Medical Devices and Instruments
3D printing technologies enable engineers and manufacturers to experiment with many ideas without requiring extra resources or escalating costs. Many manufacturers these days combine 3D printers and 3D printing filaments to produce innovative medical devices and surgical instruments. They can further evaluate the pros and cons of every 3D-printed prototype before starting mass production. Also, 3D printing technologies enable manufacturers to produce innovative devices in low-volume and on-demand.
Futuristic Operating Rooms
Many hospitals and clinics have already started transforming and modernizing their operating rooms by integrating 3D printing technologies with next-generation technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR). The 5G technology will soon enable surgeons to perform remote surgeries. That is why; 3D printing will remain one of the key technologies that will shape the future of surgery by setting up futuristic operating rooms.
Research Knowledge Improvement
In addition to facilitating the development of futuristic and automated operating rooms, 3D printing technologies have been improving the professional skills and research knowledge of physicians and surgeons consistently. Many healthcare companies already invest in new-generation 3D printers to foster and drive research and development (R&D). The latest 3D printers help doctors to diagnose health problems, plan surgeries, and produce patient anatomy in a different way. Many experts believe that 3D printing will change the way physicians get medical education and training in the near future.
According to BusinessWire.com, “The 3D printing market in the healthcare industry is poised to grow by $2.53 billion during 2021-2025, progressing at a CAGR of almost 18% during the forecast period.” Many healthcare providers will leverage 3D printing benefits to enhance productivity and curtail costs. That is why; new use cases will be created regularly that will drive the 3D printing application in medicine and surgery.
No comments:
Post a Comment