You
have the option to choose from a wide range of consumer and industrial
3D printers. Every 3D printer produces three-dimensional objects by
depositing filament layer by layer based on computer-aided design (CAD).
But every 3D printer is driven by a different and specific additive
manufacturing technology. 3D printers driven by selective laser
sintering (SLS) technology produce various items using a high-power
laser as the primary power source. They use laser light to sinter
finely-powdered filament like nylon and polyamide.
According to Wikipedia, “Selective laser sintering (SLS) is an additive manufacturing (AM) technique that uses a laser as the power source to sinter powdered material (typically nylon or polyamide), aiming the laser automatically at points in space defined by a 3D model, binding the material together to create a solid structure.”
SLS
3D printing is often described as a modern additive manufacturing
technology. But the 3D printing technology is currently used widely by
manufacturers and 3D printing service providers
for the purpose of low-volume production of components and rapid
prototyping. That is why; you need to differential SLS 3D printing from
other widely used 3D printing technology while comparing the 3D
printers. It is also important to understand the important aspect of
this additive manufacturing technology.
Understanding Important Aspects of SLS 3D Printing Technology
3D Printing Process
This
3D printing technology produces solid items based on the powder
sintering principle. An SLS 3D printer consolidates small particles of
the powdered filament using a high-powerful laser. The laser produces a
mass by sintering the powdered material based on the CAD. The 3D printer
preheats the filament to a temperature that is below the melting point.
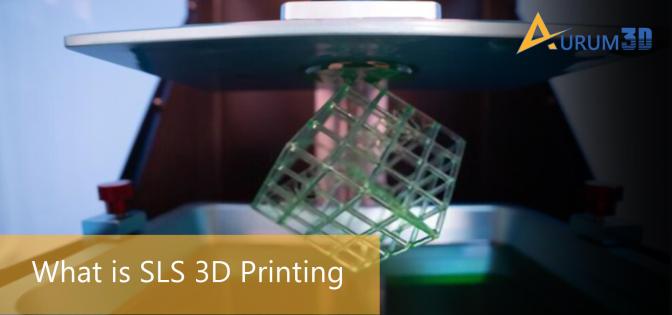
The preheating makes it easier for the laser to form solid parts by increasing the temperature level. The item to the 3D-printed is supported by the unfused powder filament. Hence, SLS 3D printing eliminates the need for a support structure. After forming the solid structure, the build chamber is cooled down for several minutes.
The cooling process ensures that the item retains the desired mechanical properties along with eliminating the chances of warping. Finally, the item is removed from the build chamber for post-processing. The 3D engineers clean the excess powder before getting the item delivered. Also, they can recycle and use the unfused filament in the future without escalating the overall 3D printing cost.
Materials/Filaments
While using an SLS 3D printer, you have the option to choose from a wide range of powdered filaments – plastic, ceramic, glass, and metal. Hence, you need to choose the SLS 3D printing filament according to the nature and needs of the item to be 3D-printed. However, you must remember that the quality of the 3D-printed object will vary according to the key attributes of the particles – shape, size, density, porosity, and roughness.
Many engineers opt for various types of polymer while using this type of 3D printer to leverage their sintering properties or behavior. They can easily customize the 3D-printed item’s mechanical properties by choosing the appropriate form of polymer. Most engineers these days avoid metals while working with SLS 3D printing technology. Instead, they use selective laser melting (SLM) technology to 3D-printed objects using metal filaments.
Advantages
At present, SLS is one of the widely used industrial 3D printing technologies. As mentioned earlier, this 3D printing technology produces solid objects without requiring support structures. The engineers and manufacturers can choose appropriate filament to produce parts that resist chemicals. Also, they can customize the 3D-printed part’s strength, stiffness, and finishing by choosing from a slew of options.

SLS produces prototypes and functional parts much faster than other 3D printers. An engineer can use a single SLS 3D printer to produce parts with complex geometries and reliable mechanical properties. Also, he can use this 3D printing technology to deliver ready-to-use parts and components with varying functionality, durability, and strength.
Disadvantages
Like other 3D printing technologies, SLS also has several shortcomings or disadvantages. Often porous surfaces are cited as one of the major shortcomings of items produced using SLS 3D printers. The engineers have to perform elaborate post-processing to deliver a fully functional part that can be used for various purposes. However, the latest SLS 3D printers reduce both time and cost by overcoming some of these shortcomings. Also, engineers can easily leverage SLS 3D printing technology using the right type of SLS 3D printer.
Evolution
SLS is one of the 3D printing technologies that have been evolving consistently. The new-age SLS 3D printers feature advanced sintering machines like FORMIGA P 110. They decrease the low-volume 3D printing cost significantly by supporting larger build sizes. Also, they distribute temperature across the build area more efficiently. You must invest in a new-age SLS 3D printer to produce medium-sized prototypes and functional parts with complex geometries using various powdered filaments.
Applications/Use Cases
At
present, SLS 3D printing is used widely by manufacturers to produce
prototypes and functional parts with complex geometries and reliable
mechanical properties. It enables engineers to produce and evaluate
prototypes by reducing 3D printing time and cost. Also, the engineers
can use SLS 3D printers to facilitate low-volume production of
components and parts for clients from various industries – automotive,
aerospace, medical, and military.
SLS is one of the advanced 3D printing technologies that leverage high-power lasers as the primary energy source. That is why; this category of 3D printers is used only in industrial and commercial setups. Individual users find it challenging to install and use SLS 3D printers for home use. But the popularity of SLS 3D printing technology has been increasing consistently across industries. However, the engineers have the option to choose from several types of SLS 3D printers according to the nature and requirements of the items to be 3D-printed.
SLS 3D printing is one of the modern additive manufacturing technologies. SLS 3D printers are used widely by manufacturers to create custom parts and perform rapid prototyping without increasing cost. But you must remember that SLS 3D printing technology, like other additive manufacturing technologies, has its own advantages and disadvantages.
References
https://formlabs.com/asia/blog/what-is-selective-laser-sintering/
https://www.materialise.com/en/manufacturing/3d-printing-technology/laser-sintering
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Selective_laser_sintering
https://www.3dsystems.com/resources/information-guides/selective-laser-sintering/sls
https://www.sinterit.com/what-is-sls-3d-printing/
https://www.axisproto.com/materials/sls/
https://www.sculpteo.com/en/materials/sls-material/
https://amfg.ai/2020/01/21/the-evolution-of-sls-new-technologies-materials-and-applications/
No comments:
Post a Comment